Biofertilizers Explained: The Ecofriendly way to Healthier Harvest
टेबल ऑफ कंटेंट
Have you ever heard your grandparents speak about how farming was different in their time? They probably engaged in more natural methods with much less of the chemical-dense fertilizers we see today. Well, what if I were to tell you that scientists have figured out a way to return to that natural way - with a neat, modern twist? Welcome to the world of biofertilizers!
So, what are biofertilizers? You can think of biofertilizers as microorganisms in a power of liquid form. When you put this into the soil or into seeds, it helps the plant grow stronger and healthier. Biofertilizers are essential to sustainable farming. Let's understand why they are important and how you can use them in your fields
Why Are Biofertilizers So Important?
Let's talk about the importance of biofertilizers. Biofertilizers are like a bank to the soil. Similar to the bank if you keep taking the money out without putting anything back, then you will eventually run out. Similar to it, the chemical fertilizers are like taking a quick loan; they can give a boost, but damage the soil in the long run.
Biofertilizers help the soil to become nutrient-rich naturally. It helps to improve soil health, protect water sources, and is budget-friendly for the farmers. This is why the importance of biofertilizers is growing every day.
The Super Team: Types of Biofertilizers
Just like we have different players in a cricket team—batsmen, bowlers, and wicket-keepers—there are different types of biofertilizers, each with a special job. Let's meet the star players.
1. The Nitrogen Squad:
These biofertilizers have bacteria that can take nitrogen, which plants need desperately but can't use from the air, and convert it into a form plants can easily absorb.
-
Rhizobium Biofertilizer: This is a classic example of a biofertilizer. Rhizobium biofertilizer is a superstar for pulses like chana, moong, and arhar. These bacteria live in the roots of these plants, forming small nodules. Inside these nodules, they work as a factory, converting atmospheric nitrogen into plant food.
-
Azospirillum Biofertilizer: This is another great example of a biofertilizer. Azospirillum biofertilizer is more of a freelancer. It doesn't live inside root nodules but around the roots of crops like wheat, rice, and millets. It also fixes nitrogen and produces growth-promoting substances, making the root system stronger.
2. The Phosphorus Gang:
Phosphorus is a very important nutrient for the crops. More often than it gets locked up in the soil. These phosphorus-based biofertilizers act like a key, unlocking it for the plants.
-
Mycorrhizal Biofertilizer: It is one of the most famous examples of biofertilizers. It is like a fungus whose thread-like structure act as an extension for the plant’s roots. These biofertilizer has a symbiotic relationship with the plants and helps them to absorb nutrients
3. Bio NPK:
You may have noticed "NPK" on fertilizer bags, which refers to nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Although there isn't a single microbe for all three elements, Bio NPK is a reference that indicates a combination of biofertilizers that provide these nutrients together.
4. Other Cool Members:
-
Blue Green Algae (BGA): Also known as cyanobacteria, these are a boon for paddy fields. They float in the water, perform photosynthesis, and fix nitrogen, enriching the entire field.
-
Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria (PSB): Bacteria like Pseudomonas and Bacillus break down the locked phosphorus in the soil, making it available for all types of crops.
Quick Links
How Are Biofertilizers Made? The Inside Scoop
Components of Biofertilizers are pretty straightforward. The main component is the beneficial microbe itself (like Rhizobium or Azospirillum). To prepare them, scientists first grow these microbes in large laboratories in a special nutrient broth. Once they have multiplied into billions, they are mixed with a sterile carrier material—usually something like peat, lignite, or charcoal powder—which helps keep them alive and makes them easy to store and transport. This final mixture, packed in bags, is what we use as biofertilizers.
Matching the Right Helper to the Crop
Just as you wouldn't use a cricket bat to play football, we can't use any biofertilizer on any crop. This is the classification of biofertilizers according to crops.
-
For Pulses (Chana, Moong, etc.): Use Rhizobium biofertilizer.
-
For Cereals (Wheat, Rice, Maize): Use Azospirillum biofertilizer.
-
For Fruits, Vegetables, and Plantation Crops (Tomato, Brinjal, Coconut): Mycorrhizal biofertilizer works wonders.
-
For Paddy/Rice: Blue Green Algae and Azospirillum are perfect.
How to Use Them? Applications of Biofertilizers
Applying biofertilizers is simple! They are not like chemicals that you just dump in the soil. They are living things and need a little care.
-
Seed Treatment: The biofertilizer is mixed with water to make a slurry, and seeds are coated in this mixture before sowing.
-
Seedling Root Dip: For crops like rice and tomato, the seedlings' roots are dipped in a solution of biofertilizer before being planted.
-
Soil Application: The biofertilizer is mixed with compost and then spread directly in the field.
The Good and The Not-So-Good
Advantages of Biofertilizers:
-
They are eco-friendly and help to reduce the chemicals in the ground.
-
They help to improve soil health for the long term
-
They are cost-effective for farmers.
-
They do not cause pollution to the water bodies or land.
Disadvantages of Biofertilizers:
-
Bio fertilizers are not a quick fix. They take time to show results
-
They require specific storage conditions and have a shorter shelf life.
-
They are crop-specific, so you need to choose the specific one.
-
Biofertilizers' effectiveness mainly depends on soil temperature, moisture, and organic matter.
Conclusion
Biofertilizers like rhizobium biofertilizer, azospirillum biofertilizer, and mycorrhizal biofertilizer are not just alternatives; they are the future of farming. They help you to grow the food while taking care of the soil. By understanding and using these amazing natural tools, you can ensure a healthier planet for generations to come.
कैटेगरी
और ब्लॉग पढ़ें
Poultry farming is the practice of raising birds for commercial profit and personal consumption. These birds primarily include chickens, ducks, turkeys, and geese that are raised on farms. Farmers engage in poultry farming to produce eggs or meat products for the...
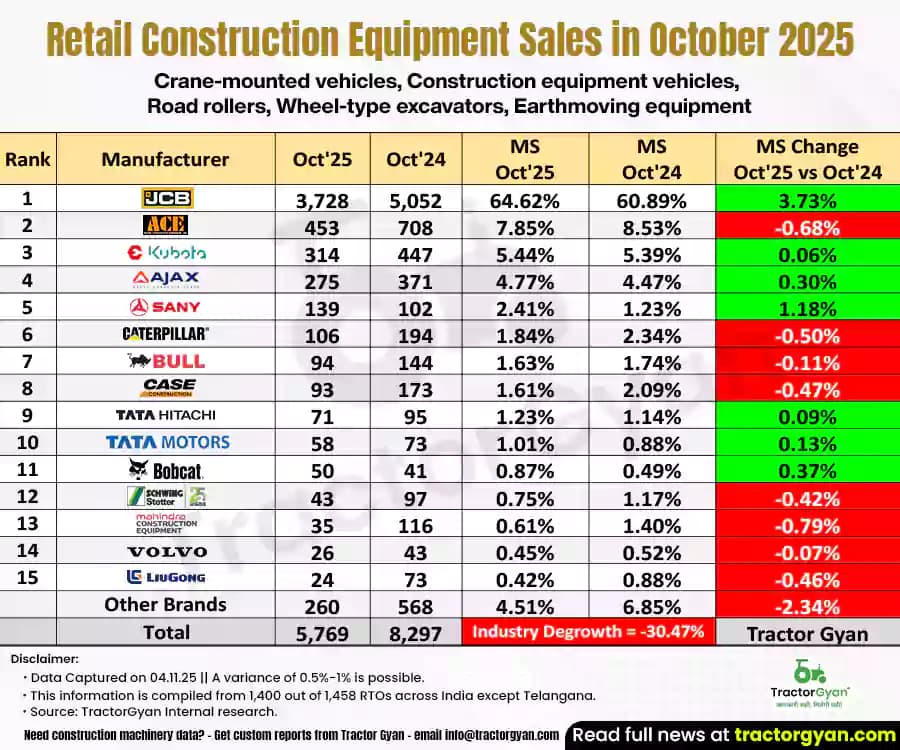
India’s construction equipment industry experienced a slowdown in October 2025, as total retail sales fell to 5,769 units, down from 8,296 units in October 2024, a 30.47% year-on-year (YoY) decline. Let’s take a closer look at how the sector performed in October 2025,...
हाल ही में रायपुर और आसपास के क्षेत्रों में बेमौसम बारिश और मौंथा तूफान ने किसानों की उम्मीदों पर पानी फेर दिया है। बनरसी और माना बस्ती जैसे इलाके, जहां नहर के किनारे धान की खेती होती है, वहां फसलें पूरी...
इसके बारे में अपनी टिप्पणी लिखें Biofertilizers Explained: The Ecofriendly way to Healthier Harvest
.webp&w=1920&q=75)
ट्रैक्टर और कृषि से जुड़े सबसे अधिक खोजे जाने वाले ब्लॉग्स
07 Jan 2026
18 Dec 2025
29 Jul 2025
08 Sep 2025
03 Jul 2025
30 Jul 2025
30 Jul 2025
30 Jul 2025
29 Jul 2025
30 Jul 2025
09 Feb 2026
31 Jul 2025
18 Dec 2025
26 Dec 2025


















.webp&w=2048&q=75)










.webp&w=2048&q=75)
.webp&w=2048&q=75)






















